Bridge Pattern - Object Persistence API Example - Java Sourcecode
Java Source Code Example for the Bridge Design Pattern - Object Persistence API
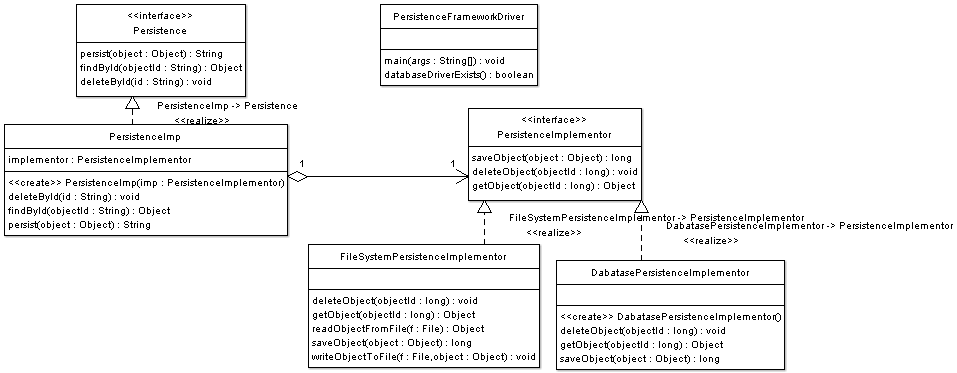
We consider the case of a persistence API can have many implementations depending on the presence or absence of a relational database, a file system, as well as on the underlying operating system.
The code below illustrates the Abstraction interface
package bridge;
/**
* Persistence Interface
* Abstraction Interface
*/
public interface Persistence {
/**
* @param object
* @return returns objectID
*/
public String persist(Object object);
/**
*
* @param objectId
* @return persisted Object
*/
public Object findById(String objectId);
/**
*
* @param id
*/
public void deleteById(String id);
}
|
The code below illustrates the Abstraction Imp:
package bridge;
/**
* Abstraction Imp
*/
public class PersistenceImp implements Persistence {
private PersistenceImplementor implementor = null;
public PersistenceImp(PersistenceImplementor imp) {
this.implementor = imp;
}
@Override
public void deleteById(String id) {
implementor.deleteObject(Long.parseLong(id));
}
@Override
public Object findById(String objectId) {
return implementor.getObject(Long.parseLong(objectId));
}
@Override
public String persist(Object object) {
return Long.toString(implementor.saveObject(object));
}
}
|
The code below illustrates the Implementor interface
package bridge;
/**
* Implementor Interface
*/
public interface PersistenceImplementor {
public long saveObject(Object object);
public void deleteObject(long objectId);
public Object getObject(long objectId);
}
|
The code below illustrates file system concrete implementor:
/**
*
*/
package bridge;
import java.io.File;
/**
* Concrete Implementor
*
*/
public class FileSystemPersistenceImplementor implements PersistenceImplementor{
@Override
public void deleteObject(long objectId) {
File f = new File("/persistence/"+Long.toString(objectId));
f.delete();
return;
}
@Override
public Object getObject(long objectId) {
File f = new File("/persistence/"+Long.toString(objectId));
return readObjectFromFile(f);
}
private Object readObjectFromFile(File f) {
// open file
// and load object
//return the object
return null;
}
@Override
public long saveObject(Object object) {
long fileId = System.currentTimeMillis();
// open file
File f = new File("/persistence/"+Long.toString(fileId));
// write file to Streanm
writeObjectToFile(f,object);
return fileId;
}
private void writeObjectToFile(File f, Object object) {
// serialize object and write it to file
}
}
|
The code below illustrates the database concrete implementor.
package bridge;
public class DabatasePersistenceImplementor implements PersistenceImplementor{
public DabatasePersistenceImplementor() {
// load database driver
}
@Override
public void deleteObject(long objectId) {
// open database connection
// remove record
}
@Override
public Object getObject(long objectId) {
// open database connection
// read records
// create object from record
return null;
}
@Override
public long saveObject(Object object) {
// open database connection
// create records for fields inside the object
return 0;
}
}
|
The code below illustrates a persistence API driver, note how the choice of concrete implementor does not affect the client code , note also that extending persistence does not affect the implementor and extending the implementor does not extend the persistence.
package bridge;
public class PersistenceFrameworkDriver {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// this program needs a persistence framework
// at runtime an implementor is chosen between file system implementation and
//database implememtor , depending on existence of databse drivers
PersistenceImplementor implementor = null;
if(databaseDriverExists()){
implementor = new DabatasePersistenceImplementor();
}else{
implementor = new FileSystemPersistenceImplementor();
}
Persistence persistenceAPI = new PersistenceImp(implementor);
Object o = persistenceAPI.findById("12343755");
// do changes to the object
// then persist
persistenceAPI.persist(o);
// can also change implementor
persistenceAPI = new PersistenceImp(new DabatasePersistenceImplementor());
persistenceAPI.deleteById("2323");
}
private static boolean databaseDriverExists() {
return false;
}
}
|
|
|
